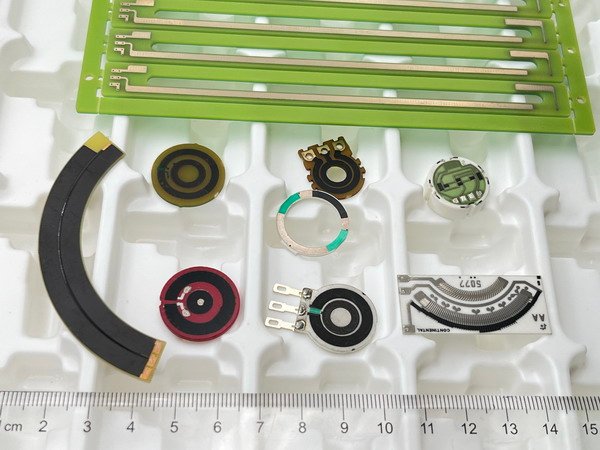
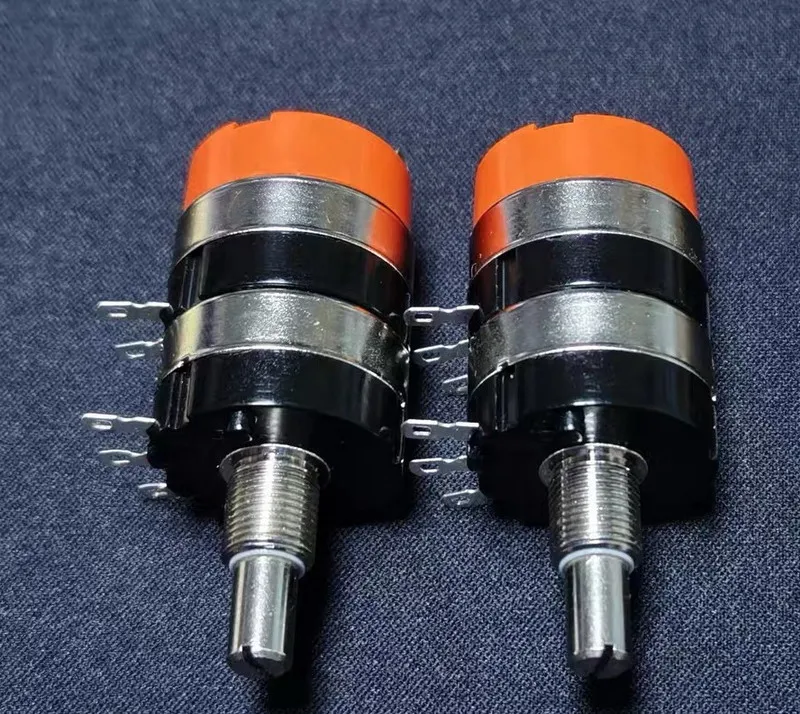
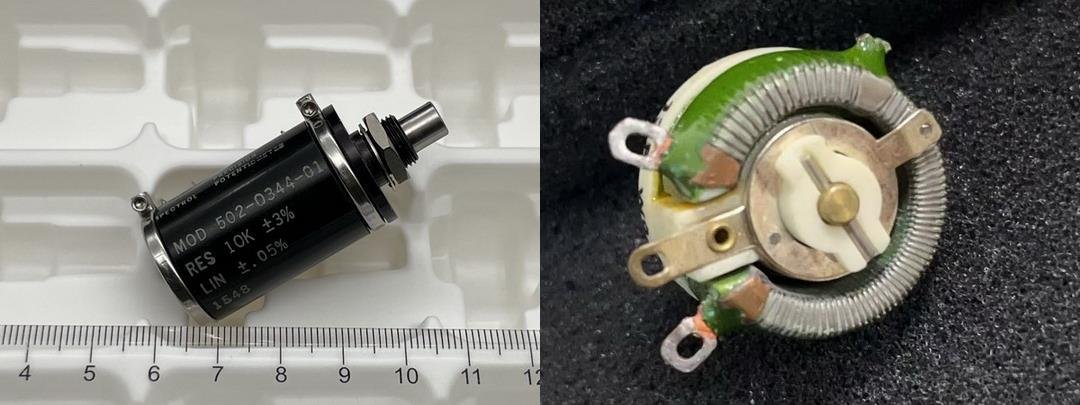
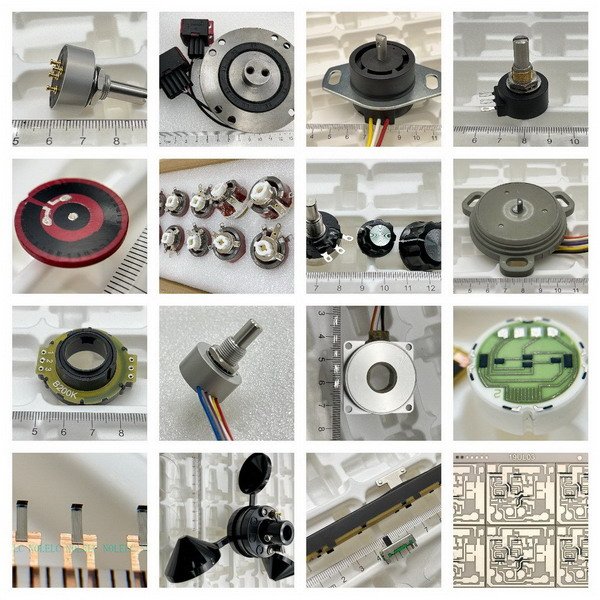
The problem: Understanding the exact purpose of a potentiometer can be confusing, especially for beginners in electronics.
A potentiometer is used to vary resistance in a circuit, often to adjust parameters like volume, brightness, or position.
Curious about how this small device achieves its versatility? Keep reading to uncover the details.
1) What is the main purpose of a potentiometer?
Potentiometers simplify control in circuits, but what is their main function?
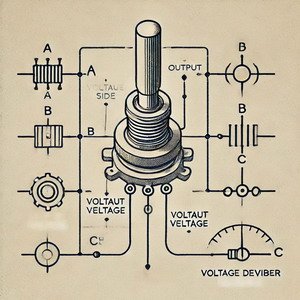
The primary purpose of a potentiometer is to act as an adjustable resistor or voltage divider1 in electrical circuits.
1.1 How It Works
Potentiometers have three terminals: one connected to a fixed resistance, the second to a wiper2 that moves along the resistive element3, and the third to the other end of the resistive path. By moving the wiper, the resistance between terminals changes, making it an effective way to control voltage and current.
1.2 Applications
| Application | Example |
|---|---|
| Audio Control | Adjusting volume in speakers |
| Light Dimmer | Controlling brightness of lamps |
| Position Sensors | Joysticks and servo motors |
The ability to fine-tune resistance makes potentiometers indispensable in electronics.
2) What would you use a potentiometer for?
Potentiometers are everywhere, but where do you see them in action?
Potentiometers are used for adjusting electrical devices, measuring voltage, and providing input in control systems.
2.1 Common Uses
- Audio Equipment: Control knobs for volume and tone adjustments.
- Measurement Tools: Measuring voltage with high precision.
- Control Systems: Acting as input devices in robotics and gaming joysticks.
2.2 Example: Gaming Joysticks
In gaming, potentiometers track the position of the joystick, translating movement into electronic signals. This ensures smooth control in applications like video games and drones.
3) What is a potentiometer for dummies?
Potentiometers might sound technical, but they are simple to understand!
A potentiometer is a dial or slider that adjusts electrical current in a device.
3.1 Breaking It Down
Think of a potentiometer as a faucet for electricity. Just as you control water flow with a tap, you control electrical flow with this device. The "wiper" inside moves across a resistive strip, changing how much electricity flows through.
3.2 Everyday Analogy
- Volume Knob: Like turning a knob to adjust speaker volume.
- Light Dimmer: Sliding to change room brightness.
Understanding potentiometers is as simple as grasping these common examples.
4) What is the potentiometer method used for?
The potentiometer method4 plays a vital role in precise measurements, but what does it do?
The potentiometer method is used to measure unknown voltages by comparing them with a known reference voltage.
4.1 How It Works
This method relies on balancing a circuit. An unknown voltage is compared to a standard cell until the current drops to zero, ensuring high accuracy.
4.2 Key Features
- No current flows through the voltage source being measured.
- Eliminates errors due to internal resistance of the source.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| High Precision | Accurate measurements |
| Zero Current Draw | Minimal impact on the circuit |
Potentiometer methods are crucial in laboratories and calibration setups.
5) Conclusion
Potentiometers serve as adjustable resistors and voltage dividers, offering versatile control in electronics for applications like audio tuning, measurement, and precision voltage control.