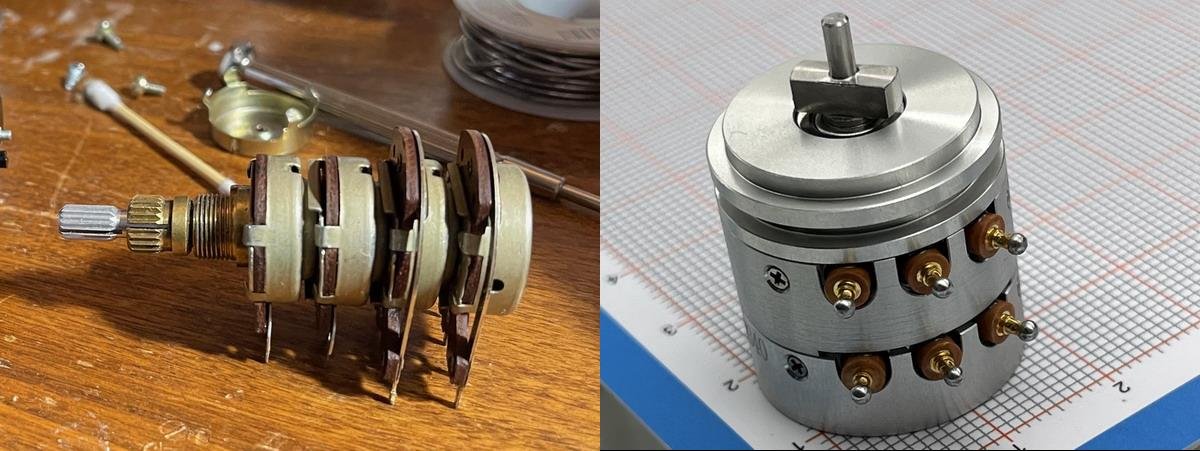
Servo potentiometers are crucial in precision systems, yet their operation often confuses many. Struggling with understanding their purpose? Let’s demystify their role step-by-step.
A servo potentiometer is a device that combines a potentiometer with a servo motor1 to provide accurate positional feedback for control systems.
Keep reading to learn how servo potentiometers work and their importance in various applications.
1) How to wire a servo with a potentiometer?
Wiring a servo with a potentiometer can be daunting if you're new to electronics. Understanding the wiring helps ensure proper functionality.
To wire a servo with a potentiometer, connect the potentiometer’s terminals to power, ground, and input pins of a control board or circuit.
1.1 Understanding the connections
The potentiometer has three terminals:
- Power (VCC): Connects to the power supply.
- Ground (GND): Connects to the ground line of the system.
- Wiper (Signal): Outputs the adjustable resistance value to the servo controller.
1.2 Example wiring table:
| Component | Connection Pin | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Servo motor | Signal pin (PWM)2 | Receives control signal. |
| Potentiometer | Wiper (Signal output) | Provides position feedback. |
| Microcontroller | Analog input pin | Reads potentiometer output. |
Proper wiring ensures the servo motor adjusts its position accurately based on the potentiometer's feedback.
Below is a simplified text/ASCII wiring diagram in English, showing how to connect a servo motor, a potentiometer, and a microcontroller (e.g., an Arduino). The diagram is followed by an explanation of each connection and a sample Arduino code.
+5V (from MCU or power supply)
|
| ┌────────────────────┐
| | POTENTIOMETER |
| | (POT) |
| | ┌──────────┐ |
| VCC──+────┤ VCC ├────┘
| | └──────────┘
| GND──+───────────────┐
| | ┌──────────┐ | (Middle pin: Wiper)
| └──┤ GND ├─┐
| └──────────┘ |
| |
| (Analog output from middle pin)
| v
| ┌─────┐
| | A0 | (MCU analog input)
| └─────┘
|
| (PWM output from MCU)
| ┌─────┐
| | D9 | (MCU PWM pin, for example)
| └─────┘
| |
| └──> SERVO signal (usually orange/yellow)
|
┌───────────────────────────────────┐
| SERVO |
| (Typically 3 wires: +5V, GND, |
| and Signal/PWM) |
| |
| +5V (red) ──────────────────┴───> +5V
| GND (black/brown) ───────────┴───> GND
| Signal (orange/yellow) <─────┘ from MCU PWM (D9)
└───────────────────────────────────┘Explanation of Connections
Potentiometer (POT)
VCC Pin → +5V (power supply from the microcontroller)
GND Pin → GND (common ground)
Wiper (middle pin) → Analog input on the microcontroller (e.g., A0)
Servo Motor
Red (V+) → +5V power supply
Black or Brown (GND) → GND (common ground)
Orange or Yellow (Signal) → Microcontroller PWM pin (e.g., D9 on Arduino)
Microcontroller (MCU)
Provides +5V and GND to both the servo and the potentiometer
Reads the potentiometer voltage (0–5V) from the wiper pin on an analog input (e.g., A0)
Outputs a PWM signal on a digital pin (e.g., D9) to control the servo’s position.
2) What does a potentiometer do in a motor?
When integrated with a motor, a potentiometer’s role becomes pivotal in enabling precise control and feedback.
In a motor, a potentiometer provides feedback on the shaft's position, helping to maintain accurate movement control.
2.1Dive deeper: Motor control through feedback
Potentiometers act as position sensors. By monitoring the motor shaft's angle, they enable:
- Accurate positioning: Ensures precise movement for tasks requiring high accuracy.
- Feedback loops: Supports closed-loop systems3 for dynamic adjustments.
2.2 Applications in motion control:
| Application | Role of Potentiometer |
|---|---|
| Robotic arms | Provides angle feedback. |
| Servo mechanisms | Maintains target positions. |
| CNC machines4 | Ensures precision alignment. |
Without potentiometers, motors would struggle with accurate positioning in dynamic environments.
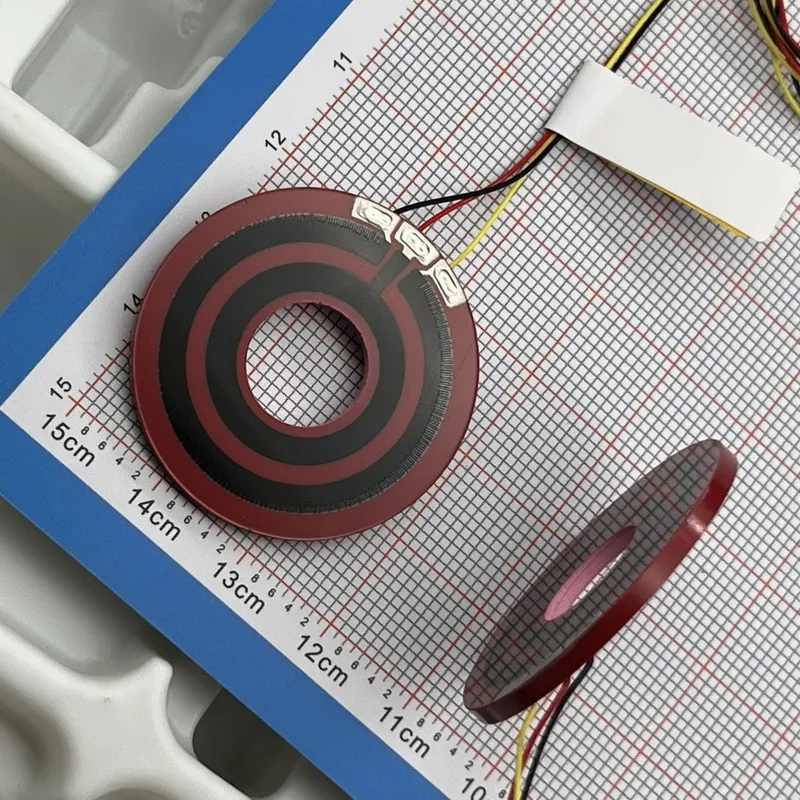
3) How does a feedback potentiometer5 work?
Feedback potentiometers simplify positional tracking by translating mechanical motion into electrical signals. Their design is both simple and effective.
A feedback potentiometer works by varying resistance based on its wiper's position, generating an output voltage proportional to movement.

Linear Variable Differential Transformer
3.1 Breaking down the operation
- Rotational input: Movement of the potentiometer’s shaft or slider.
- Resistance change: Alters electrical resistance along its resistive element6.
- Voltage output: Produces a variable voltage reflecting positional changes.
3.2 Example voltage-output table:
| Wiper Position (%) | Resistance (Ω) | Output Voltage (V) |
|---|---|---|
| 0% (start) | Low | 0.0 |
| 50% (mid-point) | Medium | 2.5 |
| 100% (end) | High | 5.0 |
This simple mechanism enables accurate feedback for control systems, making feedback potentiometers indispensable in automation.
4) Is a potentiometer a sensor or actuator?
The dual-role potential of potentiometers often sparks debate, but their primary function is clear.
A potentiometer is a sensor, as it measures and provides feedback on position or movement by varying resistance.
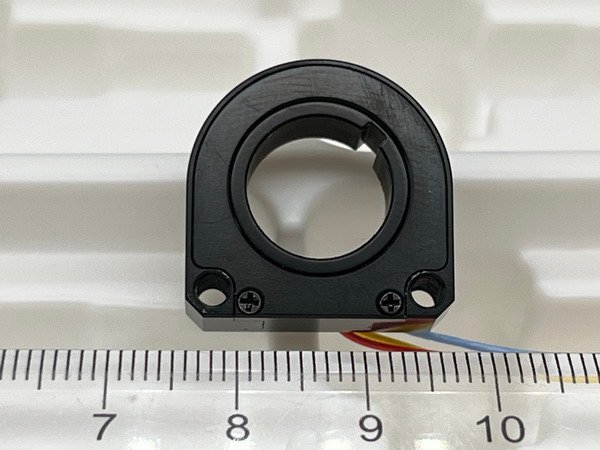

Hollow Angle Position Sensor
4.1 Dive deeper: Sensor functionality
Potentiometers are classified as sensors due to their role in:
- Data acquisition: Capturing positional data.
- Signal generation: Producing output signals for processing.
4.2 Comparison table:
| Characteristic | Sensor | Actuator |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Measures position/motion | Executes movement/action |
| Example Device | Potentiometer | Servo motor |
While a potentiometer gathers data, an actuator like a servo motor acts on that data to produce movement.
5) Conclusion
Servo potentiometers are essential in precise control systems, serving as sensors to provide critical feedback for motors and automation tasks. Their simplicity and reliability make them indispensable in robotics, industrial automation, and beyond.
-
Why servo motors matter for precise position control. ↩
-
Reason PWM signals are important for accurate servo control. ↩
-
Explanation of how closed-loop systems use real-time feedback to optimize motor performance. ↩
-
Understand how CNC machines achieve highly accurate movements using potentiometer feedback. ↩
-
Learn why the term feedback potentiometer refers to sensing mechanical motion for control. ↩
-
Explore how a resistive element converts mechanical movement into variable electrical output. ↩