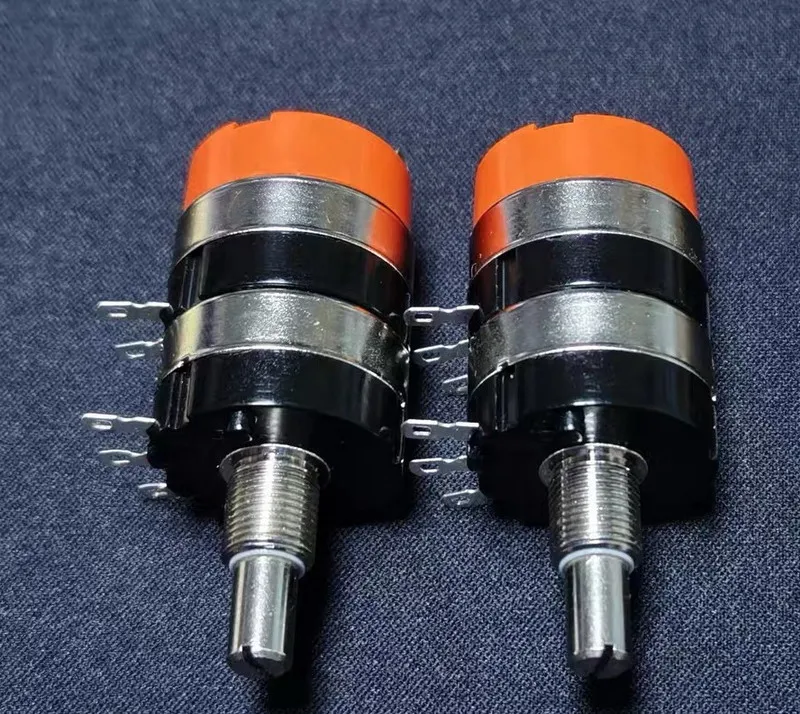
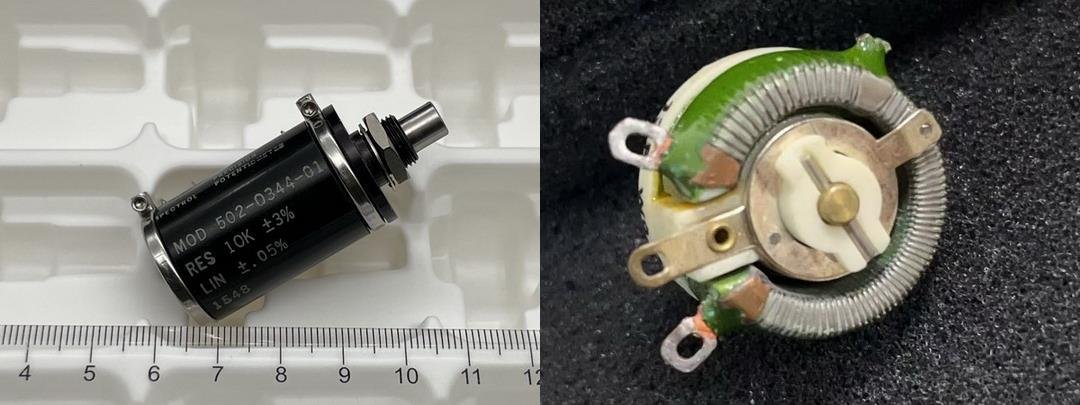
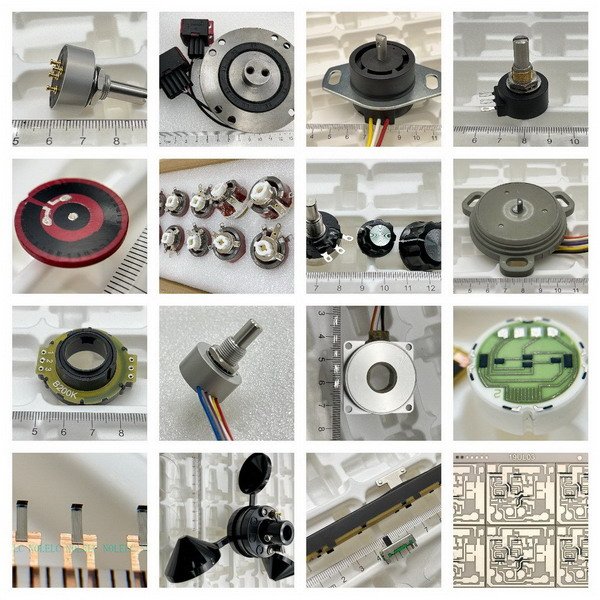
Servo angle sensors are crucial for precise control in servo systems, ensuring accurate feedback and performance in various applications.
Introduction to Servos
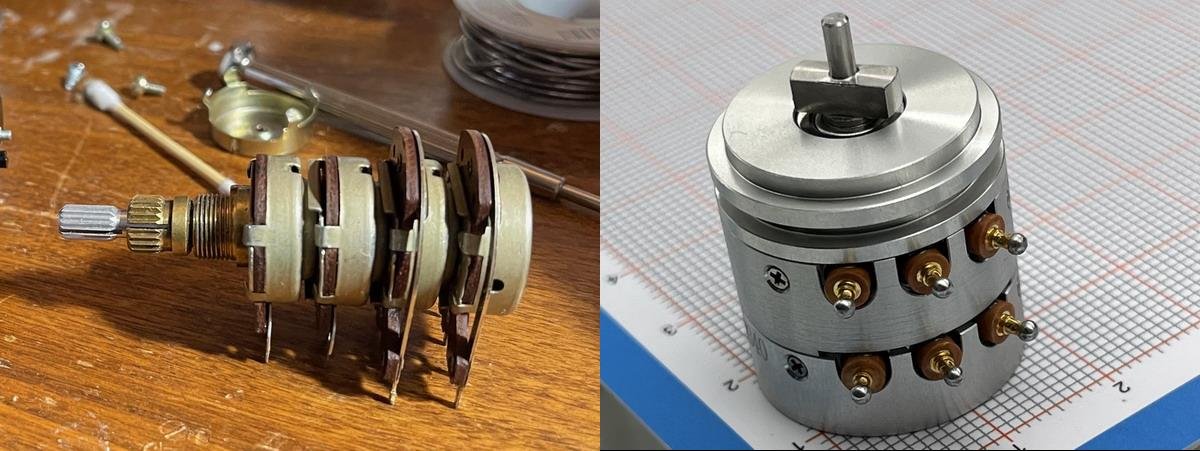
A servo is a position (angle) servo actuator suitable for control systems requiring continuous and maintainable angle changes. The basic components consist of a control circuit, motor, gear set, bearing, and servo angle sensor.
Servo as a Closed-Loop Control System
The servo is a closed-loop control system. The control circuit board receives control signals from the signal line, which directs the motor to rotate. The motor drives a series of gears that, after deceleration, transmit motion to the output servo disc. The output shaft of the servo is connected to the position servo angle sensor. As the servo disc rotates, it moves the position servo angle sensor, which outputs a voltage signal to the control circuit board for feedback. The control circuit board then determines the motor's direction and speed based on the current position, achieving the target stop. In this process, the servo angle sensor is an indispensable important component in the servo system, forming a complete power control system with the control circuit.
Performance and Features of Servo Angle Sensors
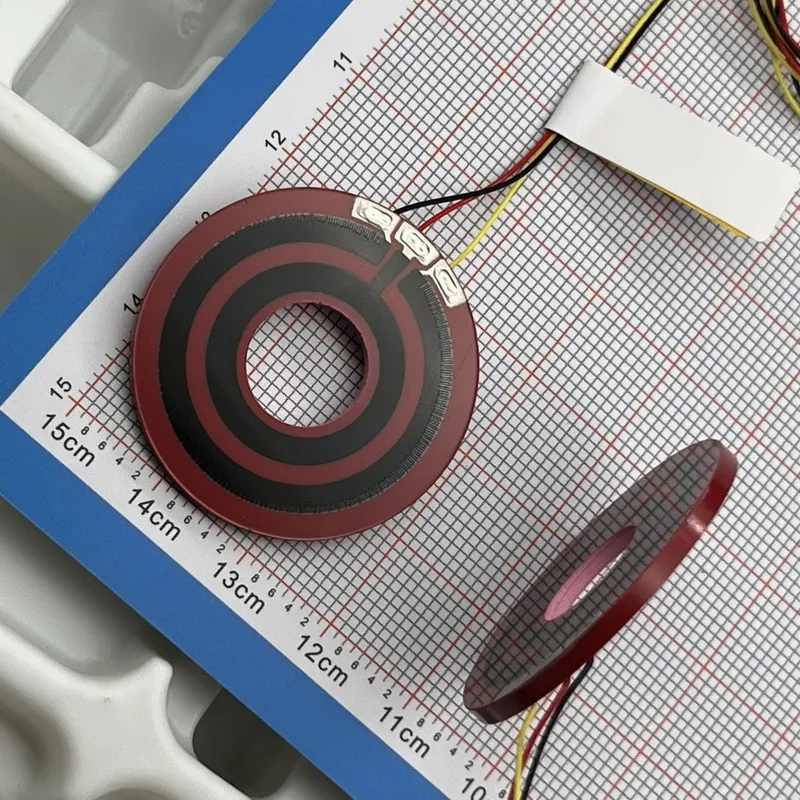
Servo angle sensors or servo potentiometers can currently achieve a low temperature coefficient of 100 ppm, a long lifespan of 5 million mechanical rotations, a decay coefficient of 0.5, and operate in environments ranging from -55°C to 125°C. They have a smoothness of 0.2, a resolution of 0.02 degrees, and can withstand over 4000G+. Some special potentiometers can also have radiation resistance characteristics and resistance to oil and thinner.
A high-performance servo system must be equipped with high-performance potentiometers/sensors. These special servo potentiometers can be widely used in maritime and aerospace fields.